ArgoWorkflow教程(三)---使用 Artifacts 实现步骤间文件共享

上一篇我们分析了 Workflow、WorkflowTemplate、template 之间的关系。本篇主要分析如何在 argo-workflow 中使用 S3 存储 artifact 实现步骤之间的文件共享。
本文主要解决两个问题:
- 1)artifact-repository 如何配置
- 2)Workflow 中如何使用
1. artifact-repository 配置
ArgoWorkflow 对接 S3 实现持久化,依赖于 artifact-repository 配置。
有三种方式设置相关配置:
- 1)全局配置:在 workflow-controller deploy 中直接通过配置文件方式写入 S3 相关配置,指定全局使用的artifactRepository, 该方式优先级最低,可以被后续两种方式替换。
- 2)命名空间默认配置:ArgoWorkflow 会在 Workflow 所在命名空间寻找当前命名空间的默认配置,该方式配置优先级第二,可以覆盖全局指定的配置。
- 规定:会在 Workflow 所在命名空间寻找名为 artifact-repositories 的 Configmap 作为配置。
- 3)Workflow 中指定配置:还可以在 Workflow 中显式指定使用哪个 artifact-repository,该方式优先级最高。
注意📢:不管什么方式指定 artifact-repository,其中存储 S3 AKSK 信息的 Secret 都必须同步到 Workflow 所在的命名空间才行。
优先级 InWorkflowConfig > Namespace > Global
全局配置
以 helm 方式部署的 ArgoWorkflow 的话默认就会以这种形式指定配置。
workflow-controller 的 deployment yaml 如下:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: argo-workflow-argo-workflows-workflow-controller
namespace: argo-dev
spec:
template:
metadata:
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --configmap
- argo-workflow-argo-workflows-workflow-controller-configmap
- --executor-image
- quay.io/argoproj/argoexec:v3.4.11
- --loglevel
- info
- --gloglevel
- "0"
- --log-format
- text
可以看到在启动命令中以 --configmap argo-workflow-argo-workflows-workflow-controller-configmap 方式指定了配置文件来源的 Configmap。
这个 Configmap 的内容如下:
apiVersion: v1
data:
# ... 省略
artifactRepository: |
s3:
endpoint: minio.default.svc:9000
bucket: argo
insecure: true
accessKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: secretKey
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argo-workflows-workflow-controller-configmap
namespace: argo
包括了 S3 的 endpoint、bucket、aksk 等信息,借助这些信息 Workflow 就可以访问 S3 了。
命名空间默认配置
根据当前实现,ArgoWorkflow 会优先使用 Workflow 所在命名空间下的默认 artifactRepository 配置。
默认会使用名为 artifact-repositories 的 Configmap 作为当前命名空间下 Workflow 的 artifactRepository 配置,Configmap 中的内容大概长这样:
注意:Configmap 名必须是 artifact-repositories
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
# If you want to use this config map by default, name it "artifact-repositories". Otherwise, you can provide a reference to a
# different config map in `artifactRepositoryRef.configMap`.
name: artifact-repositories
annotations:
# v3.0 and after - if you want to use a specific key, put that key into this annotation.
workflows.argoproj.io/default-artifact-repository: my-artifact-repository
data:
my-artifact-repository: |
s3:
bucket: lixd-argo
endpoint: minio.argo-dev.svc:9000
insecure: true
accessKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: secretKey
# 可以写多个 Repository
my-artifact-repository2: ...
Data 中的每一个 Key 对应一个 Repository, 然后使用 workflows.argoproj.io/default-artifact-repository annotation 来指定默认使用哪个 artifactRepository。
比如这里就指定了 my-artifact-repository 为默认 artifactRepository.
Workflow 中指定配置
除此之外,还可以直接在 Workflow 中指定具体要使用哪个 artifactRepository。
spec:
artifactRepositoryRef:
configMap: my-artifact-repository # default is "artifact-repositories"
key: v2-s3-artifact-repository # default can be set by the `workflows.argoproj.io/default-artifact-repository` annotation in config map.
需要指定 Configmap 以及具体的 Key 来找到唯一的 artifactRepository。
只会在当前命名空间下找,因此需要确保这个 Configmap 存在。
或者直接把 S3 配置写到 Workflow 里(不推荐),就像这样:
templates:
- name: artifact-example
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: my-input-artifact
path: /my-input-artifact
s3:
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
bucket: my-aws-bucket-name
key: path/in/bucket/my-input-artifact.tgz
accessKeySecret:
name: my-aws-s3-credentials
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-aws-s3-credentials
key: secretKey
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: my-output-artifact
path: /my-output-artifact
s3:
endpoint: storage.googleapis.com
bucket: my-gcs-bucket-name
# NOTE that, by default, all output artifacts are automatically tarred and
# gzipped before saving. So as a best practice, .tgz or .tar.gz
# should be incorporated into the key name so the resulting file
# has an accurate file extension.
key: path/in/bucket/my-output-artifact.tgz
accessKeySecret:
name: my-gcs-s3-credentials
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-gcs-s3-credentials
key: secretKey
region: my-GCS-storage-bucket-region
container:
image: debian:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["cp -r /my-input-artifact /my-output-artifact"]
只会在当前命名空间下找,因此需要确保这个 Configmap 存在。
小结
包括三种方式:
- 1)全局配置
- 2)命名空间默认配置
- 3)Workflow 中指定配置
注意📢:由于 S3 AKSK 以 Secret 方式存储,因此三种配置方式都需要将该 Secret 同步到 Workflow 所在命名空间,否则无法在 Pod 中使用,导致 Workflow 无法正常运行。
如果 ArgoWorkflow 能自动接管就好了,可以使用 https://github.com/mittwald/kubernetes-replicator 来自动同步
三种方式的区别:
- 全局配置全局只需要一个 Configmap 来指定 S3 信息即可,所有 Workflow 都使用该 S3 配置,简单,但是不够灵活。
- 命名空间默认配置:该方式可以为不同命名空间配置不同的 S3,但是需要在每个命名空间都创建一个 Configmap。
- Workflow 中指定配置:这种方式最灵活,可以为不同 Workflow 指定不同 S3,但是需要创建很多 Configmap。
使用场景:
如果全局只有一个 S3 配置,那就使用 全局配置方式,最简单。
如果租户间使用命名空间隔离,使用不同 S3,那使用命名空间默认配置方式就刚好
以上都不满足的时候,才建议使用 Workflow 中指定配置方式。
2. Workflow 中使用 artifact
key-only-artifacts
当 Workflow 中不显式指定 S3 配置信息时,argo 会按照前面的优先级自动寻找 artifact-repository 配置。
优先使用 Namespace 下的配置,没有则使用全局配置
一个完整的 Demo 如下:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: artifact-passing-
spec:
entrypoint: artifact-example
templates:
- name: artifact-example
steps:
- - name: generate-artifact
template: whalesay
- - name: consume-artifact
template: print-message
arguments:
artifacts:
# bind message to the hello-art artifact
# generated by the generate-artifact step
- name: message
from: "{{steps.generate-artifact.outputs.artifacts.hello-art}}"
- name: whalesay
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["cowsay hello world | tee /tmp/hello_world.txt"]
outputs:
artifacts:
# generate hello-art artifact from /tmp/hello_world.txt
# artifacts can be directories as well as files
- name: hello-art
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt
- name: print-message
inputs:
artifacts:
# unpack the message input artifact
# and put it at /tmp/message
- name: message
path: /tmp/message
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["cat /tmp/message"]
第一个步骤,通过
第一个步骤,通过 tee 命令创建了一个文件并通过 outputs 进行输出,由于指定的是 artifacts,因此这个文件会被存储到 S3。
然后第二个步骤指定 inputs.artifacts 从 S3 读取名为 message 的 artifact 并存储到 /tmp/message 目录。
问题来了第二步中读取的 artifact 是从哪儿来的呢,就是 steps 中通过 arguments.artifacts 指定的,通过 name 进行关联。
整个逻辑和 parameter 基本一致
1)whalesay template 通过 outputs.artifacts 来申明当前 template 会输出一个 artifact。
2)print-message 中通过 inputs.artifacts 申明需要一个 artifact,并指定存储位置
3)steps 在使用该 template 时,通过 arguments.artifacts 来指定一个 artifact,这个 artifact 来源就是 1 中的 output,通过
{{steps.generate-artifact.outputs.artifacts.$name}}语法引用。
artifact-passing-vzp2r-1469537892:
boundaryID: artifact-passing-vzp2r
displayName: generate-artifact
finishedAt: "2024-03-29T08:42:34Z"
hostNodeName: lixd-argo
id: artifact-passing-vzp2r-1469537892
message: 'Error (exit code 1): You need to configure artifact storage. More
information on how to do this can be found in the docs: https://argo-workflows.readthedocs.io/en/release-3.5/configure-artifact-repository/'
name: artifact-passing-vzp2r[0].generate-artifact
artifact 压缩
默认情况下,所有的 artifact 会被打成 tar 包并 gzip 压缩,可以通过archive 字段来配置压缩情况:
- 默认行为:tar + gzip
- 可选关闭 tar+ gzip
- 或者配置 gzip 压缩等级
<... snipped ...>
outputs:
artifacts:
# default behavior - tar+gzip default compression.
- name: hello-art-1
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt
# disable archiving entirely - upload the file / directory as is.
# this is useful when the container layout matches the desired target repository layout.
- name: hello-art-2
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt
archive:
none: {}
# customize the compression behavior (disabling it here).
# this is useful for files with varying compression benefits,
# e.g. disabling compression for a cached build workspace and large binaries,
# or increasing compression for "perfect" textual data - like a json/xml export of a large database.
- name: hello-art-3
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt
archive:
tar:
# no compression (also accepts the standard gzip 1 to 9 values)
compressionLevel: 0
<... snipped ...>
Artifact 垃圾回收
所有 Artifact 都会上传到 S3,为了保证 S3 不被填满,垃圾清理是个问题。
好消息是,argo-workflow 3.4 开始,可以在 Workflow 中添加配置来实现自动删除不需要的 Artifacts。
当前提供两种回收策略,分别是:
OnWorkflowCompletion:工作流运行完成后就删除OnWorkflowDeletion:工作流被删除时才删除
同时可以统一为 Workflow 中的所有 artifact 配置回收策略,也可以单独为每一个 artifact 配置回收策略。
Demo 如下:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: artifact-gc-
spec:
entrypoint: main
artifactGC:
strategy: OnWorkflowDeletion # default Strategy set here applies to all Artifacts by default
templates:
- name: main
container:
image: argoproj/argosay:v2
command:
- sh
- -c
args:
- |
echo "can throw this away" > /tmp/temporary-artifact.txt
echo "keep this" > /tmp/keep-this.txt
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: temporary-artifact
path: /tmp/temporary-artifact.txt
s3:
key: temporary-artifact.txt
- name: keep-this
path: /tmp/keep-this.txt
s3:
key: keep-this.txt
artifactGC:
strategy: Never # optional override for an Artifact
核心部分如下:
spec:
entrypoint: main
# 为 Workflow 中的所有 artifact 统一配置
artifactGC:
strategy: OnWorkflowDeletion # default Strategy set here applies to all Artifacts by default
# 单独指定 artifact 的回收策略
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: temporary-artifact
artifactGC:
strategy: Never # optional override for an Artifact
注意事项:为了避免相同工作流并发运行时,artifact 被误删除的问题,可以为不同工作流配置不同的 artifact repository。
forceFinalizerRemoval
argo-workflow 会启动一个 <wfName>-artgc-* 格式命名的 Pod 来执行垃圾回收工作,如果执行失败,整个 Workflow 也会被标记为失败。
同时由于finalizers 没有被删除掉
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
finalizers:
- workflows.argoproj.io/artifact-gc
会导致这个 Workflow 无法删除,可以执行以下命令移除
kubectl patch workflow my-wf \
--type json \
--patch='[ { "op": "remove", "path": "/metadata/finalizers" } ]'
为了优化体验,argo-workflow 3.5 版本新增了 forceFinalizerRemoval 参数
spec:
artifactGC:
strategy: OnWorkflowDeletion
forceFinalizerRemoval: true
只要forceFinalizerRemoval 设置为 true,即时 GC 失败也会移除 finalizers。
常用 Artifacts 扩展
除了 S3 Artifacts 之外,为了便于使用, argo-workflow 还内置了 git、http 方式来获取 artifact。
可以直接从指定 git 仓库 clone 代码,或者从指定 url 下载文件,就像这样:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: hardwired-artifact-
spec:
entrypoint: hardwired-artifact
templates:
- name: hardwired-artifact
inputs:
artifacts:
# Check out the main branch of the argo repo and place it at /src
# revision can be anything that git checkout accepts: branch, commit, tag, etc.
- name: argo-source
path: /src
git:
repo: https://github.com/argoproj/argo-workflows.git
revision: "main"
# Download kubectl 1.8.0 and place it at /bin/kubectl
- name: kubectl
path: /bin/kubectl
mode: 0755
http:
url: https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.8.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
# Copy an s3 compatible artifact repository bucket (such as AWS, GCS and MinIO) and place it at /s3
- name: objects
path: /s3
s3:
endpoint: storage.googleapis.com
bucket: my-bucket-name
key: path/in/bucket
accessKeySecret:
name: my-s3-credentials
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-s3-credentials
key: secretKey
container:
image: debian
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["ls -l /src /bin/kubectl /s3"]
3. Demo
测试点:
- 1)创建到 Workflow 对应 Namespace 是否能正常使用
- 2)将S3 配置创建到 Argo 部署的 Namespace 是不是可以不需要进行同步了。
Configmap:
- Name:argo-workflow-argo-workflows-workflow-controller-configmap
- Namespace:argo-dev
- Key:artifactRepository
Minio 准备
部署一个 local-path-storage csi,如果有别的 csi 也可以跳过这一步
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rancher/local-path-provisioner/v0.0.24/deploy/local-path-storage.yaml
然后部署 minio
helm install minio oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/minio
my-release-minio.default.svc.cluster.local
export ROOT_USER=$(kubectl get secret --namespace default my-release-minio -o jsonpath="{.data.root-user}" | base64 -d)
export ROOT_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace default my-release-minio -o jsonpath="{.data.root-password}" | base64 -d)
配置 artifact-repository
cm.yaml 完整内容如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: artifact-repositories
annotations:
workflows.argoproj.io/default-artifact-repository: my-artifact-repository
data:
my-artifact-repository: |
s3:
bucket: argo
endpoint: minio.default.svc.cluster.local:9000
insecure: true
accessKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: accessKey
secretKeySecret:
name: my-s3-secret
key: secretKey
secret.yaml 完整内容如下:
apiVersion: v1
stringData:
accessKey: admin
secretKey: minioadmin
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-s3-secret
type: Opaque
创建 artifact repository 配置
kubectl apply -f cm.yaml
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
Workflow 中使用artifact
两个步骤:
- generate:生成一个文件,并通过 outputs.artifact 写入 S3
- consume:使用 inputs.artifact 从 S3 读取文件并打印内容
workflow.yaml 完整内容如下:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: key-only-artifacts-
spec:
entrypoint: main
templates:
- name: main
dag:
tasks:
- name: generate
template: generate
- name: consume
template: consume
dependencies:
- generate
- name: generate
container:
image: argoproj/argosay:v2
args: [ echo, hello, /mnt/file ]
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: file
path: /mnt/file
s3:
key: my-file
- name: consume
container:
image: argoproj/argosay:v2
args: [cat, /tmp/file]
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: file
path: /tmp/file
s3:
key: my-file
创建 Workflow
kubectl create -f workflow.yaml
等待运行完成
[root@lixd-argo artiface]# kubectl get wf
NAME STATUS AGE MESSAGE
key-only-artifacts-9r84h Succeeded 2m30s
S3 查看文件
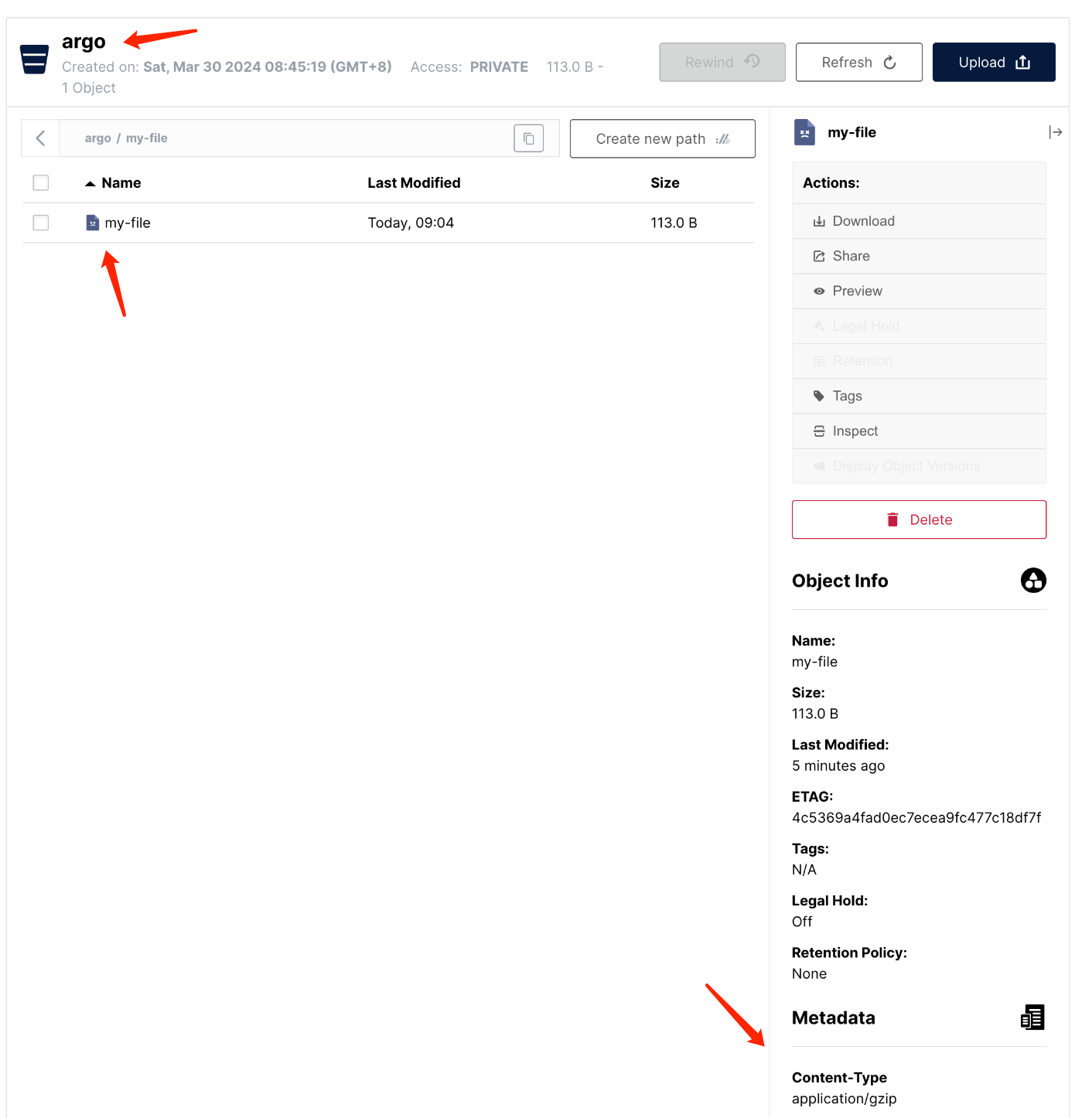
到 S3 中查看文件是否存在
可以看到,在 argo bucket 下有一个名为 my-file的文件存在,而且 context-type 是 application/gzip,这也验证了 argo 会对 artifact 执行 tar+gzip。
4. 小结
本文主要分析了 argo 中的 artifact 使用,包括如何配置 artifact-repository:
包括三种方式:
- 1)全局配置
- 2)命名空间默认配置
- 3)Workflow 中指定配置
以及如何在 Workflow 中使用 artifact 并通过一个 Demo 进行演示。